Table of Contents
Introduction
PRM Package, Packing an RPM may require while we need to build something from source. Example, If we need to install any package and it doesn’t have an RPM package the only way is to download the source, compile and install. But installing from source will be easier, however, to remove the installation from source will be a pain. To make life easier, error-free it’s good to build an RPM from the required source. In our guide let’s download OpenVPN source and start to build the RPM package.
Basic tools
This packaging guide created on a minimal operating system. So we required to install some of the basic packages.
# yum install wget curl bind-utils vim net-tools screen bash-completion -yIn case if you get any error for locale settings make sure to set the right language for you.
# localectl set-locale LC_CTYPE=en_US.utf8On a minimal installation, this will be a common issue.
Install Prerequisites
To start with building an RPM package first we need to install the required compilers and build packages with dependencies.
# yum install rpm* gcc gpg* make autoconf rng-tools openssl-devel lzop lzo-devel pam-devel zlib-devel cmake -yCreate an Unpreveileged account
To compile and build a package we should not continue from root user instead create a normal user account prior to building.
# groupadd -g 5001 pkgbuilder
# useradd -u 5001 -g 5001 -c "RPM Package Builder" -s /bin/bash pkgbuilderwe are good to move forward.
Generating GPG key
Singing our RPM package is important because the end-user need to trust your package that he is going to install from a trusted source. Before generating GPG key we need run rngd command this will create some random data, to run this command we need to log in as root account which will speed up the process. Moreover, we need to configure x11 locally in our server to enter the password during GPG key creation. So make sure to configure the X11 before moving forward.
Configure X11 forwarding
You may encounter an error if you have not configured with X11 forwarding.
# grep -i "^X11" /etc/ssh/sshd_configEdit the sshd_config and make sure to change no to yes for below two lines.
[root@vpn sbin]# grep -i "^X11" /etc/ssh/sshd_config
X11Forwarding yes
X11UseLocalhost yes
[root@vpn sbin]#Login as root user and start to run the random command to generate some random data.
# rngd -r /dev/urandomThe above command takes a few seconds to complete. By the following login as normal user to start creating GPG Key.
# su - pkgbuilder
# gpg --gen-keyDuring the process, we need to choose some options.
- First, select the kind of key as RSA by selecting 1 and press return.
- Second, Just press return to use the default value 2048.
- Third, make sure to provide a valid period else press return to use (0) unlimited.
- Fourth, confirm the values (y).
- Just a name to identify the key.
- At last Email address and comments, By following Press (O) to continue.
[pkgbuilder@vpn ~]$ gpg --gen-key
gpg (GnuPG) 2.0.22; Copyright (C) 2013 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
This is free software: you are free to change and redistribute it.
There is NO WARRANTY, to the extent permitted by law.
Please select what kind of key you want:
(1) RSA and RSA (default)
(2) DSA and Elgamal
(3) DSA (sign only)
(4) RSA (sign only)
Your selection? 1
RSA keys may be between 1024 and 4096 bits long.
What keysize do you want? (2048)
Requested keysize is 2048 bits
Please specify how long the key should be valid.
0 = key does not expire
= key expires in n days
w = key expires in n weeks
m = key expires in n months
y = key expires in n years
Key is valid for? (0)
Key does not expire at all
Is this correct? (y/N) y
GnuPG needs to construct a user ID to identify your key.
Real name: Linux Sysadmins
Email address: admin@linuxsysadmins.com
Comment: Linux Sysadmins GPG Singing Key
You selected this USER-ID:
"Linux Sysadmins (Linux Sysadmins GPG Signing Key) admin@linuxsysadmins.com"
Change (N)ame, (C)omment, (E)mail or (O)kay/(Q)uit? O
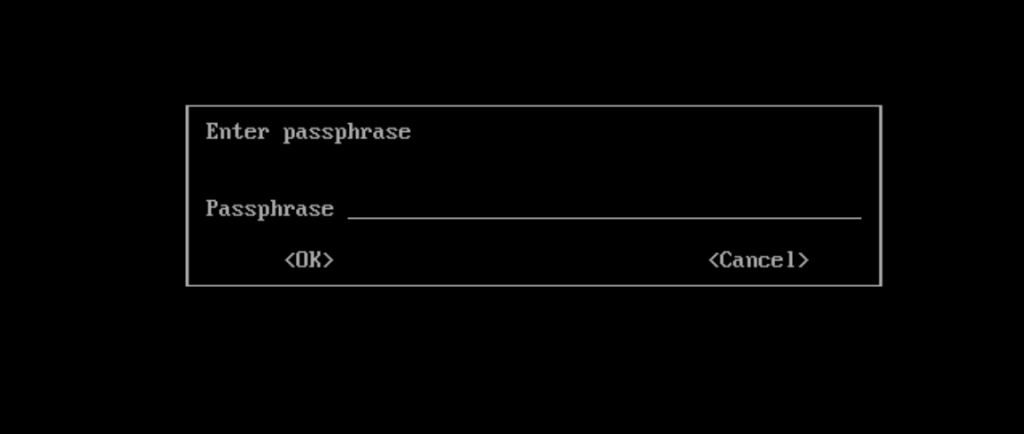
You need a Passphrase to protect your secret key.We will get a password prompt as shown in below picture enter the password and confirm the same to continue.
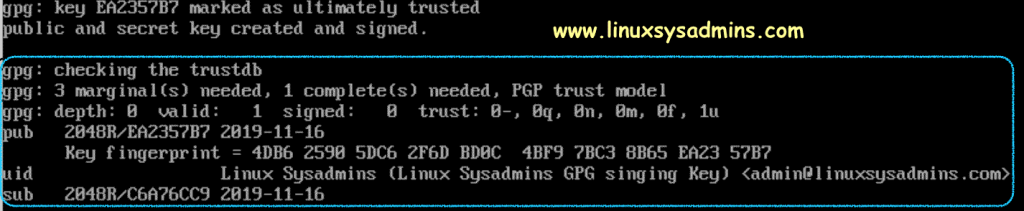
Note the above Key (EA2357B7) information for future reference.
Prepare and Build the RPM package
Rules to remember for a build configure, make and make install
Download the source file you need to build an RPM.
# wget https://swupdate.openvpn.org/community/releases/openvpn-2.4.8.tar.gzCreate the required directory structure to build the RPM. Then create the SPEC file template.
$ rpmdev-setuptree
$ rpmdev-newspec rpmbuild/SPECS/openvpn.spec
$ cp openvpn-2.4.8.tar.gz rpmbuild/SOURCES/Output for reference
[pkgbuilder@vpn ~]$ rpmdev-newspec rpmbuild/SPECS/openvpn.spec
rpmbuild/SPECS/openvpn.spec created; type minimal, rpm version >= 4.11.
[pkgbuilder@vpn ~]$ cp openvpn-2.4.8.tar.gz rpmbuild/SOURCES/A template of a spec file created, However, we need to put the required information in it.
$ vim rpmbuild/SPECS/openvpn.spec We have modified the spec file as per our requirement.
[pkgbuilder@vpn ~]$ cat rpmbuild/SPECS/openvpn.spec
Name: openvpn
Version: 2.4.8
Release: 1%{?dist}
Summary: OpenVPN is a robust and highly flexible VPN daemon.
License: GNU General Public License version 2
URL: https://openvpn.net/community-downloads/
Source0: openvpn-2.4.8.tar.gz
BuildRequires: gcc
%description
OpenVPN supports SSL/TLS security, ethernet bridging,
TCP or UDP tunnel transport through proxies or NAT,
support for dynamic IP addresses and DHCP, scalability
to hundreds or thousands of users, and portability to
most major OS platforms.
%prep
%setup -q -n %{name}-%{version}
%build
%configure
make %{?_smp_mflags}
%install
rm -rf $RPM_BUILD_ROOT
%make_install
%files
%defattr(-,root,root)
%doc README AUTHORS COPYING NEWS TODO.IPv6 ChangeLog
/usr/share/doc
/usr/include
/usr/lib64/openvpn/plugins
/usr/sbin/openvpn
/usr/share/man
%changelog
[pkgbuilder@vpn ~]$Start Building the RPM package.
$ rpmbuild -ba rpmbuild/SPECS/openvpn.specThis will unpack the tar.gz package and configure by its own and build the RPM package.
Processing files: openvpn-debuginfo-2.4.8-1.el7.x86_64
Provides: openvpn-debuginfo = 2.4.8-1.el7 openvpn-debuginfo(x86-64) = 2.4.8-1.el7
Requires(rpmlib): rpmlib(FileDigests) <= 4.6.0-1 rpmlib(PayloadFilesHavePrefix) <= 4.0-1 rpmlib(CompressedFileNames) <= 3.0.4-1
Checking for unpackaged file(s): /usr/lib/rpm/check-files /home/pkgbuilder/rpmbuild/BUILDROOT/openvpn-2.4.8-1.el7.x86_64
Wrote: /home/pkgbuilder/rpmbuild/SRPMS/openvpn-2.4.8-1.el7.src.rpm
Wrote: /home/pkgbuilder/rpmbuild/RPMS/x86_64/openvpn-2.4.8-1.el7.x86_64.rpm
Wrote: /home/pkgbuilder/rpmbuild/RPMS/x86_64/openvpn-debuginfo-2.4.8-1.el7.x86_64.rpm
Executing(%clean): /bin/sh -e /var/tmp/rpm-tmp.0Fi73d
umask 022
cd /home/pkgbuilder/rpmbuild/BUILD
cd openvpn-2.4.8
/usr/bin/rm -rf /home/pkgbuilder/rpmbuild/BUILDROOT/openvpn-2.4.8-1.el7.x86_64
exit 0
[pkgbuilder@vpn ~]$ In the above output, you can notice the package
/home/pkgbuilder/rpmbuild/RPMS/x86_64/openvpn-2.4.8-1.el7.x86_64.rpmSigning the RPM Package
Finally, its time to sign the package. List the available GPG key and assign it to our new build package.
$ gpg --list-keys
$ echo "%_gpg_name EA2357B7" >> .rpmmacros
$ rpmsign --addsign rpmbuild/RPMS/x86_64/openvpn-2.4.8-1.el7.x86_64.rpm Below output for your reference
[pkgbuilder@vpn ~]$ gpg --list-keys
/home/pkgbuilder/.gnupg/pubring.gpg
pub 2048R/EA2357B7 2019-11-16
uid Linux Sysadmins (Linux Sysadmins GPG singing Key) admin@linuxsysadmins.com
sub 2048R/C6A76CC9 2019-11-16
[pkgbuilder@vpn ~]$
[pkgbuilder@vpn ~]$ echo "%_gpg_name EA2357B7" >> .rpmmacros
[pkgbuilder@vpn ~]$
[pkgbuilder@vpn ~]$ rpmsign --addsign rpmbuild/RPMS/x86_64/openvpn-2.4.8-1.el7.x86_64.rpm
Enter pass phrase:
Pass phrase is good.
rpmbuild/RPMS/x86_64/openvpn-2.4.8-1.el7.x86_64.rpm:
[pkgbuilder@vpn ~]$Testing the package
Install the RPM
Let’s start to install our new build package by running the RPM command.
# rpm -ivh openvpn-2.4.8-1.el7.x86_64.rpm
# yum localinstall openvpn-2.4.8-1.el7.x86_64.rpmIt looks good and we had a successful installation.
[root@vpn ~]# rpm -ivh openvpn-2.4.8-1.el7.x86_64.rpm
warning: openvpn-2.4.8-1.el7.x86_64.rpm: Header V4 RSA/SHA1 Signature, key ID ea2357b7: NOKEY
Preparing… ########################## [100%]
Updating / installing…
1:openvpn-2.4.8-1.el7 ########################## [100%]
[root@vpn ~]#
Running transaction
Installing : openvpn-2.4.8-1.el7.x86_64 1/1
Verifying : openvpn-2.4.8-1.el7.x86_64 1/1
Installed:
openvpn.x86_64 0:2.4.8-1.el7
Complete!
[root@vpn ~]#Verify the RPM information
[root@vpn ~]# rpm -qa | grep openvpn
openvpn-2.4.8-1.el7.x86_64
[root@vpn ~]#
[root@vpn ~]# yum info openvpn
Installed Packages
Name : openvpn
Arch : x86_64
Version : 2.4.8
Release : 1.el7
Size : 1.2 M
Repo : installed
From repo : /openvpn-2.4.8-1.el7.x86_64
Summary : OpenVPN is a robust and highly flexible VPN daemon.
URL : https://openvpn.net/community-downloads/
License : GNU General Public License version 2
Description : OpenVPN supports SSL/TLS security, ethernet bridging,
: TCP or UDP tunnel transport through proxies or NAT,
: support for dynamic IP addresses and DHCP, scalability
: to hundreds or thousands of users, and portability to
: most major OS platforms.
[root@vpn ~]#The above information is exactly which we have given in the SPEC file.
Remove the RPM
By running yum command remove the installed package.
Running transaction
Erasing : openvpn-2.4.8-1.el7.x86_64 1/1
Verifying : openvpn-2.4.8-1.el7.x86_64 1/1
Removed:
openvpn.x86_64 0:2.4.8-1.el7
Complete!
[pkgbuilder@vpn ~]$We have completed successfully with a build, installing and removing the RPM package.
Conclusion:
Building an RPM package from the source will be a safe option. Above step by step guide helped us to build a package from the source. Subscribe to our newsletter and stay tuned for more guides.