Table of Contents
Introduction
Install MongoDB on your Server in short span of time. MongoDB is a cross-platform program, commonly referred to as a document-oriented database. It uses a JSON-like documents format. MongoDB has written in C+, Python, Go, Javascript languages.
MongoDB is one of the leading general-purpose database platforms. It was designed keeping in consideration of developers and their application needs to truly unleash the power of applications that they build. The company adopted an open-source development model in 2009 and began offering commercial support in 2013. Red Hat used MongoDB on most of its products, They have dropped using MongoDB on Debian, Fedora and Red Hat due to change in licensing part.
Read more about MongoDB
Installation Requirements
This tutorial guide only supports 64-bit systems. However, you can get information about various supported platforms, here.
Install MongoDB Packages
Supported packages are included in their MongoDB repository. It contains the following packages:
- mongodb-org-server (Contains mongod daemon + configuration file )
- mongodb-org-shell (Contains mongo shell)
- mongodb-org-tools (Contains mongo backup and management tools)
- mongodb-org-mongos (Contains mongos daemon)
- mongodb-org (Will install all above components)
Method 2: Starting the Installation
Creating repo file in /etc/yum.repos.d/ directory, like below:
$ sudo vi /etc/yum.repos.d/mongodb-org-4.0.repoAdd the following in the newly created repo file:
[mongodb-org-4.0]
name=MongoDB Repository
baseurl=https://repo.mongodb.org/yum/amazon/2013.03/mongodb-org/4.0/x86_64/
gpgcheck=1
enabled=1
gpgkey=https://www.mongodb.org/static/pgp/server-4.0.asc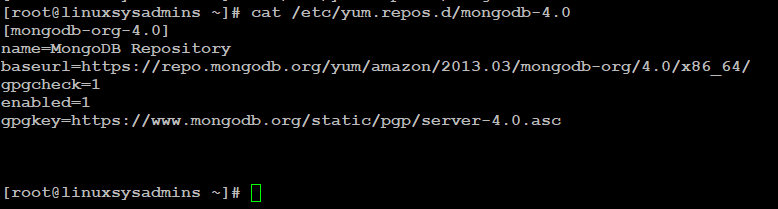
After successfully creating the required repo file, you can begin installation and verify the installed version by the following command:
$ sudo yum install -y mongodb-org
$ sudo mongod --versionConfiguring MongoDB
After installing the MongoDB package, you can configure it as per your need. Configuration file location (default): ‘/etc/mongod.conf’
$ cat /etc/mongod.conf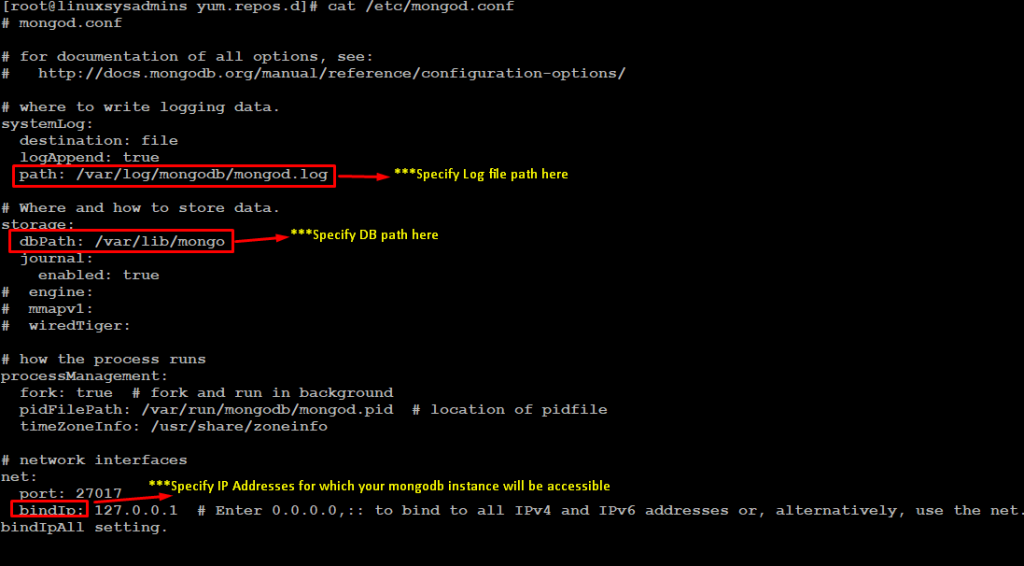
MongoDB Default Settings
By default, MongoDB runs through mongod user account and uses the following default directories for database storage path and logs file path.
- /var/lib/mongo (the data directory)
- /var/log/mongodb (the log directory)
Through this process, the default directory paths are created as above and the owner and group for these directories are set to “mongod”.
Method 2: Install Mongo DB from a tarball
Download the MongoDB tarball package from MongoDB Download Center.
Extract the downloaded tar file.
$ sudo tar -zxvf mongodb-linux-x86_64-amazon2-4.0.5.tgzSet Path Variable for MongoDB
Now you can either copy the downloaded binaries into a directory which is already set as your PATH variable i.e /usr/local/bin or
Modify your user’s PATH environment variable to include this directory like edit your shell’s initialization script (e.g ~/.bashrc):
export PATH=<monogodb-install-dir-path>/bin:$PATHFor this replace with your extracted MongoDB archive path respectively
Through this process, the default directory paths are not created. So you can create them as follows:
# mkdir -p /var/lib/mongo
# mkdir -p /var/log/mongodbBy default, MongoDB runs through mongod user account. So after creating user “mongod”, set the owner and group of these directories as follows:
# chown -R mongod:mongodTo use Non-Default locations
You can also edit the MongoDB configuration file i.e /etc/mongod.conf and set the DB path and log path as per your requirement.
storage.dbPath (specify a new db path)
systemLog.path (specify a new log file path)Starting MongoDB
After successfully installing the MongoDB, start it by the following command and make sure to persistently start the service during reboot.
$ sudo systemctl start mongod
$ sudo systemctl enable mongod
$ sudo systemctl status mongodUsing MongoDB Shell
Start using MongoDB via mongo shell on your machine as the
Additional information
In case if you found any bug in MongoDB you can submit your bug report through below URL.
https://github.com/mongodb/mongo/wiki/Submit-Bug-ReportsConclusion
You can install MongoDB server by using any one of the above-mentioned methods. In the up-coming tutorial, we will cover the replication in MongoDB and also about backups and restore procedures. So make sure to subscribe to our newsletter and begin your journey to become a MongoDB expert.