Table of Contents
Introduction
Setting up HAProxy for Kubernetes high availability involves configuring HAProxy as a load balancer to distribute incoming traffic across multiple Kubernetes control plane nodes. HAProxy ensures redundancy and fault tolerance by directing requests to healthy nodes, thereby enhancing the availability and reliability of the Kubernetes cluster. This setup optimizes resource utilization and ensures continuous operation even if individual nodes experience failures, thereby supporting seamless scaling and robust performance for containerized applications.
If you are looking to set up a Kubernetes Cluster on your favourite distro, refer below internal URLs
- Creating Highly Available Clusters with kubeadm on Rocky Linux 9.4
- Install Kubernetes Cluster on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS using kubeadm
- Install Kubernetes Cluster with Ansible on Ubuntu in 5 minutes
- How to Install a Kubernetes on CentOS 7
- Upgrade Kubernetes Cluster with zero downtime in 5 easy steps
- Create a Rolling Update Kubernetes Deployment in 3 ways
Setting up HAProxy
Set the hostname
# hostnamectl set-hostname haproxy.linuxsysadmins.lanInstall the package to configure the HAProxy
# dnf install haproxy -yMake sure to backup the original configuration prior to the changes.
# cp /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg-originalWe have defined status to check the traffic, frontend and backend for the Kubernetes HA setup.
#---------------------------------------------------------------------
# Global settings
#---------------------------------------------------------------------
global
log 127.0.0.1 local2
chroot /var/lib/haproxy
pidfile /var/run/haproxy.pid
maxconn 4000
user haproxy
group haproxy
daemon
# turn on stats unix socket
stats socket /var/lib/haproxy/stats
# utilize system-wide crypto-policies
ssl-default-bind-ciphers PROFILE=SYSTEM
ssl-default-server-ciphers PROFILE=SYSTEM
#---------------------------------------------------------------------
# common defaults that all the 'listen' and 'backend' sections will
# use if not designated in their block
#---------------------------------------------------------------------
defaults
mode http
log global
option dontlognull
option http-server-close
option redispatch
retries 3
timeout http-request 10s
timeout queue 1m
timeout connect 5000
timeout client 50000
timeout server 50000
timeout http-keep-alive 10s
timeout check 10s
maxconn 3000
# status
listen stats
bind *:9000
mode http
stats enable
stats hide-version
stats uri /stats
stats refresh 30s
stats realm Haproxy\ Statistics
stats auth admin:haproxypassword
#---------------------------------------------------------------------
# main frontend which proxys to the backends
#---------------------------------------------------------------------
frontend kube-apiserver
bind *:6443
mode tcp
tcp-request inspect-delay 5s
tcp-request content accept if { req.ssl_hello_type 1 }
default_backend kube-apiserver
#---------------------------------------------------------------------
# round robin balancing between the various backends
#---------------------------------------------------------------------
backend kube-apiserver
mode tcp
option tcp-check
balance roundrobin
default-server inter 10s downinter 5s rise 2 fall 2 slowstart 60s maxconn 250 maxqueue 256 weight 100
server k8smas1 192.168.0.21:6443 check
server k8smas2 192.168.0.22:6443 check
server k8smas3 192.168.0.23:6443 check
#---------------------------------------------------------------------Check for the Syntax error.
# haproxy -c -V -f /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfgStart and enable the HAProxy service
# systemctl start haproxy.service
# systemctl enable haproxy.serviceIncase, if the service failed to start check for the logs and remediate.
# journalctl -xeu haproxy.serviceFirewall Requirement
Allow the traffic out of the box.
# firewall-cmd --add-port={9000,6443}/tcp --permanent
# firewall-cmd --reload
# firewall-cmd --list-allService Validation
To confirm the status of HAProxy page and Kubernetes API port, do a query as follow.
# ss -tunlp | grep "9000\|6443"The status can be viewed from any web browser by navigating to HAProxy IP.
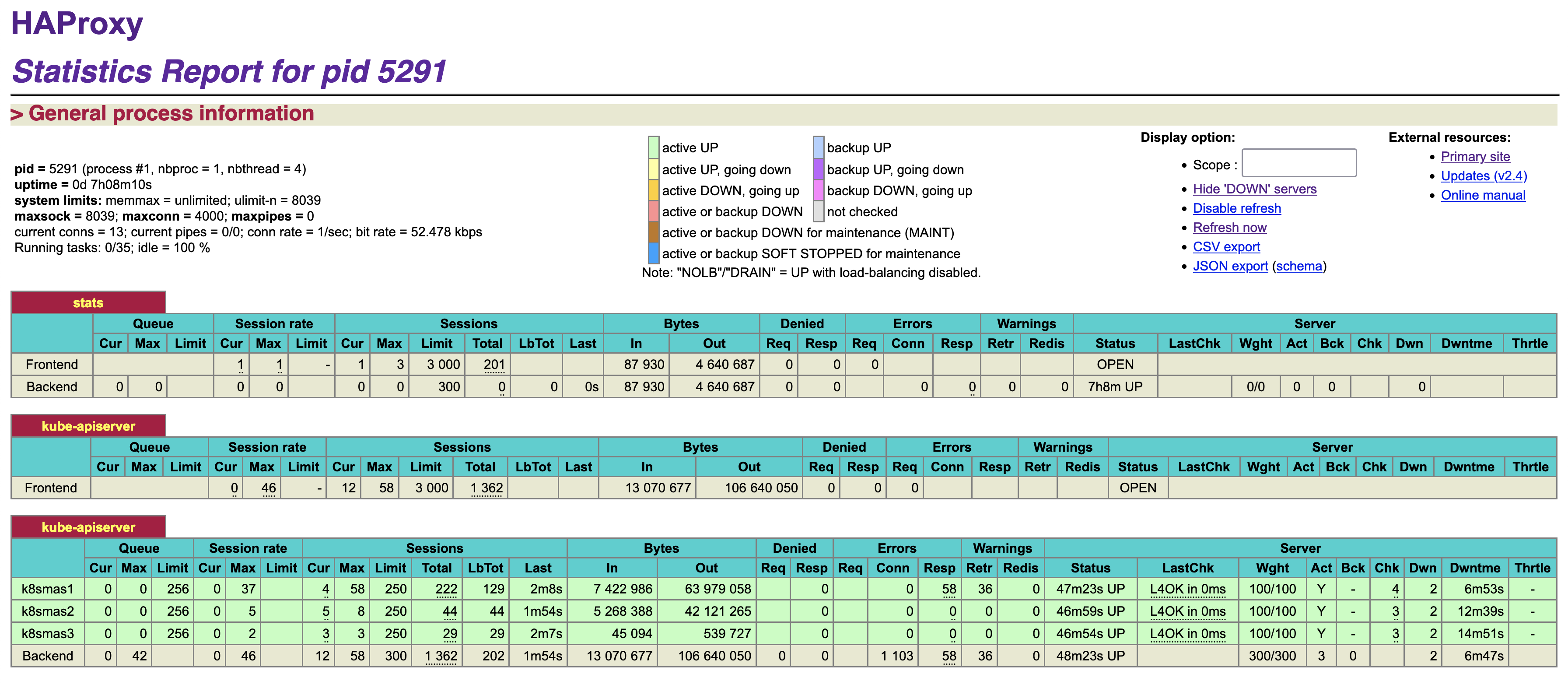
That’s it, we have completed with setting up a HAProxy Load Balancer for Kubernetes HA setup.